Operating System.5 Process Description and Control2
오퍼레이팅 시스템(운영체제) 공부
Operating System.5 Process Description and Control2
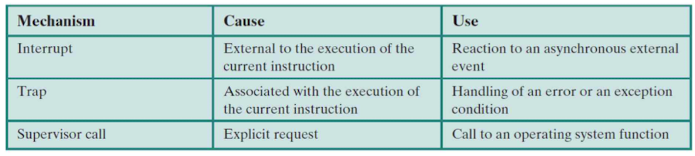
Modes of Execution
- mode bit: kernel mode와 user mode를 나타내는 정보를 저장한 bit
- kernel에서 할 수 있는 일
- mode switch : user와 kernel 사이에서 모드를 바꾸는 것
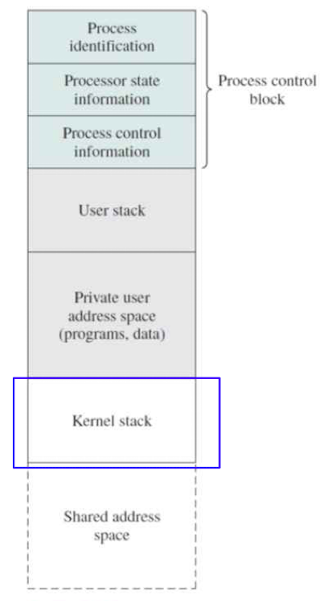
- 현대의 운영체제에서는 Process 마다 user mode와 kernel mode의 stack이 존재한다.
- kernel을 위한 code, data, stack이 필요하다.
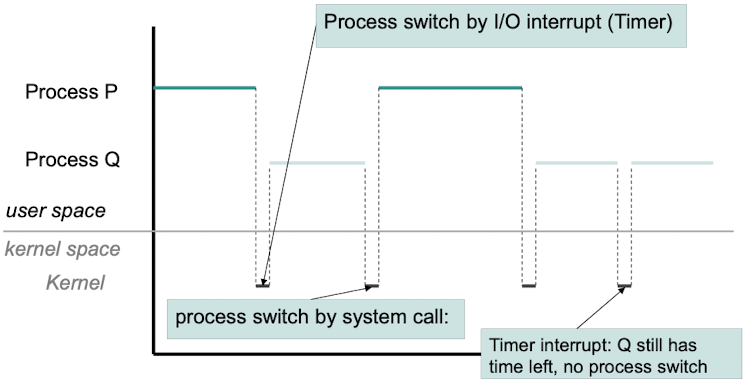
Process Switch
- process switch로 인해 발생하는 비용
- 프로세스 컨텍스트 저장 및 복원
- 캐시 무효화
- 인터럽트 처리
- TLB 플러시
- 스케줄링 오버헤드
- 캐시 트래싱
Process Creation(Directed)
- process의 context 공간 할당
- code, data를 메모리에 로딩, stack 생성
- PCB 생성 및 초기화
- process를 ready queue에 삽입
Process Creation(by Cloning and Replacing)
- cloning : 부모 프로세스로부터 복사본을 만들고, pid만 수정하여 생성->
fork()- text, data, stack, PCB를 복사
- 그 이후로 child와 parent는 서로 독립적인 스택을 보유한다.
- replacing : PID를 바꾸지 않고, code, data, heap, stack을 새로운 프로그램으로 교체 ->
exec()
Copy On Write(COW)
- shared된 page에 data 변경이 생겼을 때만 복사하는 방법
Process Termination
- Voluntary termination(자발적인 종료) :
exit(status)main()문이 끝난 경우- exit function이 실행된 경우
- Involuntary termination(비자발적 종료) :
kill(pid, signal),abort()- 부포 프로세스 혹은 OS에 의해 종료됐을 때
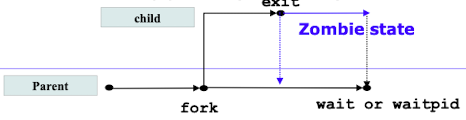
Zombie
- process는 exit()으로 종료 상태인데, kernel이 PCB를 즉시 지우지 않고 남아있는 상태
- 즉, 부모 프로세스의
wait(&status)에 의해 종료 상태 값이 parent에게 전달되기 까지의 상태- reaping : parent가 이러한 자식 프로세스의 종료 상태 값을 거둬가는 행위
Orphan
- 부모 프로세스가 자식 프로세스보다 먼저 종료하게 될 때 자식 프로세스가 가질 수 있는 상태이다.
- 보통 이러한 경우 init process로 reparent를 하게 된다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.