Java 자료구조 : Hash Table
HashTable, CS, DataStructure
Java 자료구조 : Hash Table
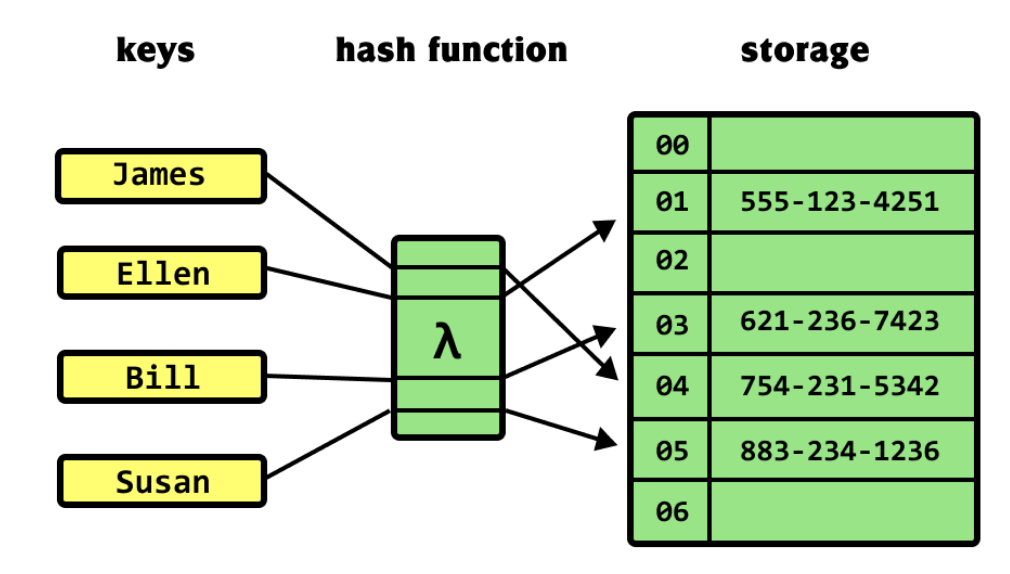
해쉬 테이블이란?
- 키(Key)에 데이터(Value)를 매핑할 수 있는 데이터 구조(이걸 Map이라고 함)
- 키는 맵에 오직 유일하게 있어야함
- 해쉬 함수를 통해, 배열에 키에 대한 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 주소(인덱스 번호)를 계산
- Key를 통해 바로 데이터가 저장되어 있는 주소를 알 수 있으므로, 저장 및 탐색 속도가 획기적으로 빨라짐
- 미리 해쉬 함수가 생성할 수 있는 주소(인덱스 번호)에 대한 공간을 배열로 할당한 후, 키에 따른 데이터 저장 및 탐색 지원
사용하는 용어
- 해쉬 함수(Hash Function): 임의의 데이터를 고정된 길이의 값으로 리턴해주는 함수
- 해쉬 (Hash), 해쉬 값(Hash Value), 또는 해쉬 주소(Hash Address): 해싱 함수를 통해 리턴된 고정된 길이의 값
- 해쉬 테이블(Hash Table): 키 값의 연산에 의해 직접 접근이 가능한 데이터 구조
- 충돌(Collision) : 해싱함수를 통해 나온 자리에 이미 다른 데이터가 저장되어 있는 경우
자료구조 해쉬 테이블의 장단점과 용도
- 장점
- 데이터 저장/읽기 속도가 빠르다. (검색 속도가 빠르다.)
- 해쉬는 키에 대한 데이터가 있는지(중복) 확인이 쉬움
- 단점
- 일반적으로 저장공간이 좀더 많이 필요하다.
- 여러 키에 해당하는 주소가 동일할 경우 충돌을 해결하기 위한 별도 자료구조가 필요함
- 주요 용도
- 검색이 많이 필요한 경우
- 저장, 삭제, 읽기가 빈번한 경우
- 캐쉬 구현시 (중복 확인이 쉽기 때문)
충돌(Collision)해결 알고리즘
- Chaining 기법
- 개방 해싱 또는 Open Hashing 기법 중 하나: 해쉬 테이블 저장공간 외의 공간을 활용하는 기법
- 충돌이 일어나면, 링크드 리스트라는 자료 구조를 사용해서, 링크드 리스트로 데이터를 추가로 뒤에 연결시켜서 저장하는 기법
- Linear Probing 기법
- 폐쇄 해슁 또는 Close Hashing 기법 중 하나: 해쉬 테이블 저장공간 안에서 충돌 문제를 해결하는 기법
- 충돌이 일어나면, 해당 hash address의 다음 address부터 맨 처음 나오는 빈공간에 저장하는 기법
- 저장공간 활용도를 높이기 위한 기법
코드 작성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
public class MyHash {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHash(Integer size) {
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot {
String key;
String value;
Slot(String key, String value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public int hashFunc(String key) {
return (int)(key.charAt(0)) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean saveData(String key, String value) {
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key) {
this.hashTable[address].value = value;
return true;
} else {
Integer currAddress = address + 1;
while (this.hashTable[currAddress] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[currAddress].key == key) {
this.hashTable[currAddress].value = value;
return true;
} else {
currAddress++;
if (currAddress >= this.hashTable.length) {
return false;
}
}
}
this.hashTable[currAddress] = new Slot(key, value);
return true;
}
} else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(key, value);
}
return true;
}
public String getData(String key) {
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key) {
return this.hashTable[address].value;
} else {
Integer currAddress = address;
while (this.hashTable[currAddress] != null) {
if (this.hashTable[currAddress].key == key) {
return this.hashTable[currAddress].value;
} else {
currAddress++;
if (currAddress >= this.hashTable.length) {
return null;
}
}
}
return null;
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
Java패키지의 HashMap
- HashMap과 사용법이 거의 동일한 컬렉션(Collection)에는 Hashtable이 있다. 두 클래스의 차이점은 Thread 관점에서 안전하냐(Hashtable), 안전하지 않은 대신 속도가 빠르냐(HashMap)이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
import java.util.HashMap;
HMap<String,Integer> map1=new HashMap();
Map<String,Integer> map2=new HashMap();
//map1 put
map1.put("map1-key1", 100);
map1.put("map1-key2", 200);
//map2 put
map2.put("map2-key3", 300);
map2.put("map2-key4", 400);
System.out.println("map1:"+map1);
System.out.println("map2:"+map2);
//map2에 map1을 합침
map2.putAll(map1); // Map<String,Integer> map2=new HashMap(map1); 처럼 생성과 동시에 넘겨줄 수도 있음
System.out.println("map2 includes map1:"+map2);
//map1의 키, 값 변경
map1.put("map1-key1", 1000);
//map2에는 영향 없음.
System.out.println("map2 includes map1:"+map2);
- KeySet 사용 예시(모든 키를 순회 가능)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap();
map.put("key1",50);
map.put("key2",100);
map.put("key3",150);
map.put("key4",200);
System.out.println("All key-value pairs");
for(String key:map.keySet()) {
System.out.println("{"+key+","+map.get(key)+"}");
}
- 참고로 람다식의 foreach도 동일하게 가능!
- 객체를 HashMap에서 Key로 사용하기 위해선 다음과 같이
equals와hashCode메서드를 Overriding- String은 이미 내부적으로 구현되어 있는 것을 활용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return name.hashCode()+id.hashCode();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return this.hashCode()==o.hashCode();
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.