Database 2. 관계형 데이터베이스의 각종 개념
데이터 베이스 이론 공부
Database 2. 관계형 데이터베이스의 각종 개념
Relational Data Model
Set
- 서로 다른 element를 가지는 collection
- 하나의 set에서 elements의 순서는 중요하지 않다
- e.g. {1, 3, 11, 4, 7}
Relation in mathematics
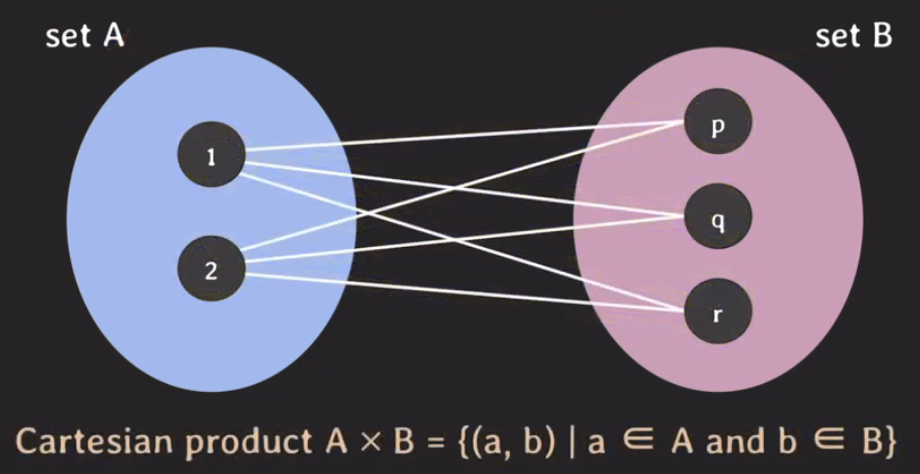
- Cartesian Product A x B : set A와 Set B에서 고를 수 있는 각각의 element에 대한 pair에 집합
- Binary Relation : Cartesian Product의 부분 집합을 의미함
- subset of Cartesian product와 set-of-tuple로 이뤄져있다.
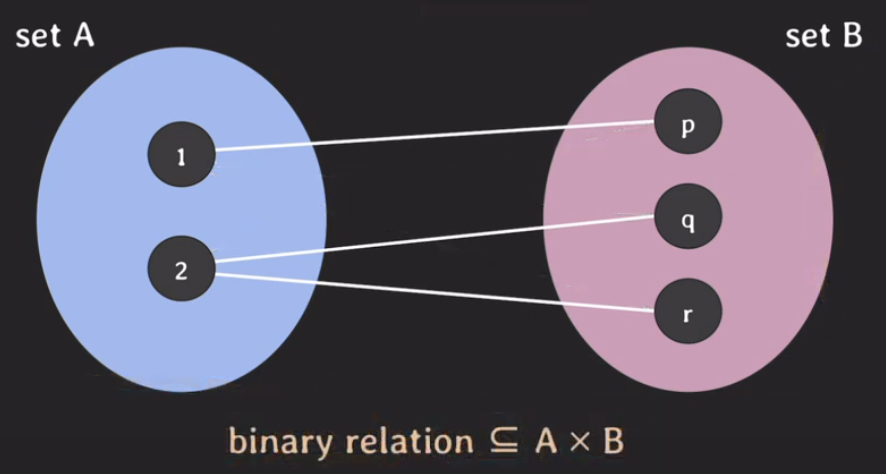
- n-ary relation
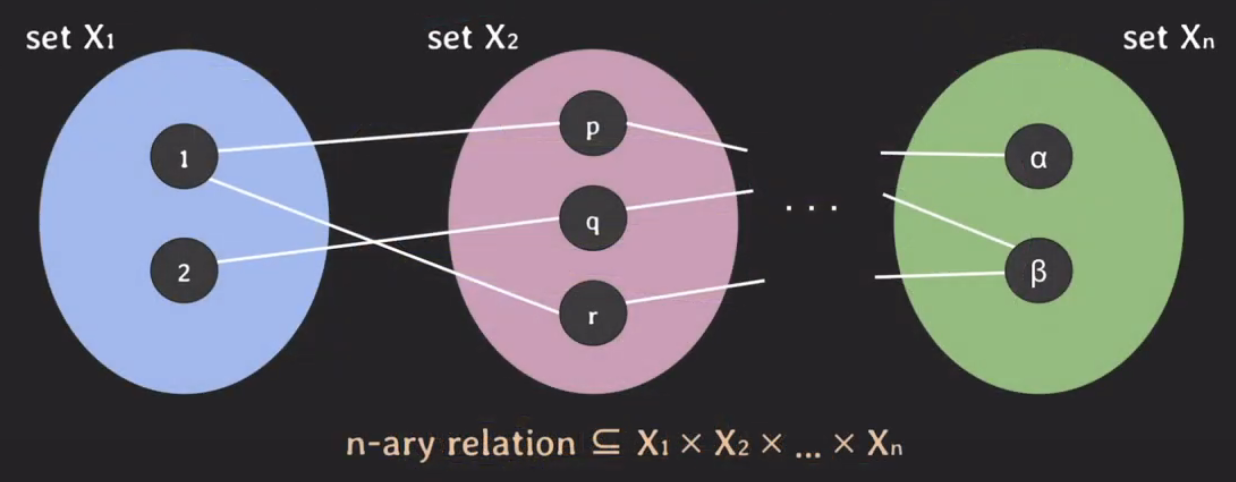
- n-tuple이라고도 부름
Relation in mathematics & relational data model
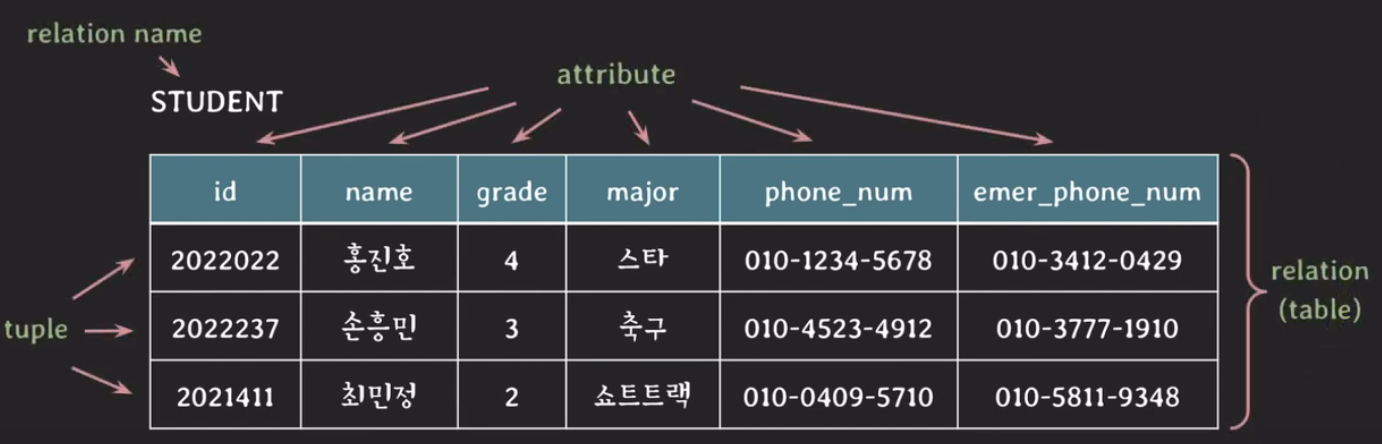
relation schema
- relation의 구조를 나타낸다.
- relation 이름과 attributes 리스트로 표기된다.
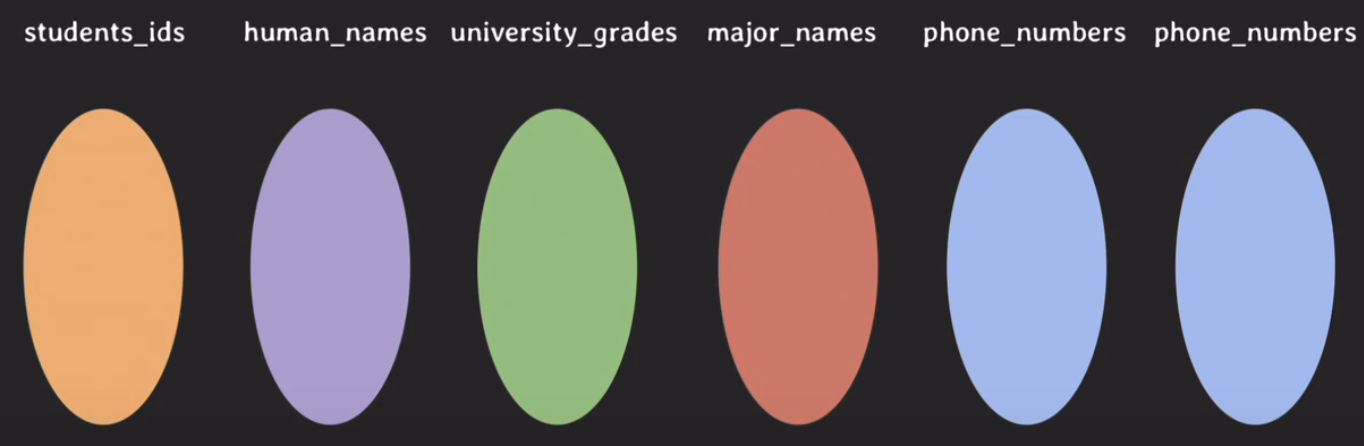
- e.g. STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num)
- attribute와 관련된 constraints도 포함한다.
- degree of relation : degree 6
- degree : relation schema에서 attributes의 수
- degree of relation : degree 6
relational database
- relational data model에 기반하여 구조화된 database
- relational database는 여러 개의 relations으로 구성된다.
relation의 특징들
- relation은 중복된 tuple을 가질 수 없다.(relation의 개념 자체가 set of tuples 이기 때문이다.)
- relation의 tuple을 식별하기 위해 attribute의 부분 집합을 key로 설정한다.
- relation에서 tuple의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
- 하나의 relation에서 attribute의 이름은 중복되면 안된다.
- 하나의 tuple에서 attribute의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
- attribute는 atomic해야 한다.(즉, composite 또는 multi-valued attribute는 허용되지 않는다.)
NULL의 의미
- 값이 존재하지 않는다.
- 값이 존재하나 아직 그 값이 무엇인지 알지 못한다.
- 해당 사항과 관련 없다.
- NULL은 많은 중의적인 의미를 갖고 있기 때문에 최대한 사용하지 않는 것이 중요하다.
Key
Super key
- relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별할 수 있는 attributes set
Candidate key
- 어느 한 attribute라도 제거하면 unique하게 tuples를 식별할 수 없는 super key
- key 또는 minimal super key
- 쉽게 말해 최소한의 집합으로 고유 식별할 수 있는 key
Primary key
- relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별하기 위해 선택된 candidate key
- e.g. PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 primary key는
- {id} 또는 {team_id, back_number}
unique key
- primary key가 아닌 candidate keys
- alternate key라고도 부름
foreign key
- 다른 relation의 PK를 참조하는 attribute set
Constraints(제약사항)
- relational database의 relations들이 언제나 항상 지켜줘야 하는 제약 사항
implicit constraints
- relational data model 자체가 가지는 constraints
- relation은 중복되는 tuple을 가질 수 없다.
- relation 내에서는 같은 이름의 attribute를 가질 수 없다.
schema-based constraints
- 주로 DDL을 통해 schema에 직접 명시할 수 있는 constraints
explicit constraints라고도 부른다.
- 종류
- domain constraints : attribute의 value는 해당 attribute의 domain에 속한 value여야 한다.
- key constraints : 서로 다른 tuples는 같은 value의 key를 가지 수 없다.
- null value constraints : attribute가 NOT NULL로 명시됐다면 NULL을 값으로 가질 수 없다.
- entity integrity constraint : primary key는 value에 NULL을 가질 수 없다.
- referential integrity constraint : FK와 PK와 도메인이 같아야 하고 PK에 없는 values를 FK가 값으로 가질 수 없다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.